Topical oxygen therapy with Granulox
Wounds cannot heal without oxygen
Chronic wounds share a common challenge: a lack of oxygen reaching the wound. Wound healing requires large amounts of oxygen
Patients with chronic wounds, such as pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers suffer from underlying conditions that compromise the body’s ability to move oxygen to the wound. The situation is worsened by a combination of reduced blood flow in the region of the wound, due to underlying diseases such as diabetes or chronic venous insufficiency, and less efficient
*Hauser CJ. Tissue salvage by mapping of skin surface transcutaneous oxygen tension index. Archives of surgery (Chicago, Ill : 1960) 1987; 122(10): 1128-30.
Oxygen therapies can be delivered from the inside or outside (topically) of the body. Both approaches influence wound healing in different ways
Oxygen provided from the inside via hyperbaric treatment improves oxygen supply thanks to improved blood oxygenation, but this effect is temporary and best used as an adjunct treatment
Oxygen provided from the outside via various topical oxygen therapy methods facilitates the availability of oxygen to the base of the wound
Topical haemoglobin treatment is a simple way to facilitate oxygen diffusion directly within a chronic wound
Controlling for condition-specific symptoms is central to healing – but this plays just one role in a host of therapies that contribute to successful healing of chronic wounds.
Using a topical, purified haemoglobin spray on hard-to-heal wounds provides a direct channel for oxygen-loaded haemoglobin to diffuse through wound exudate
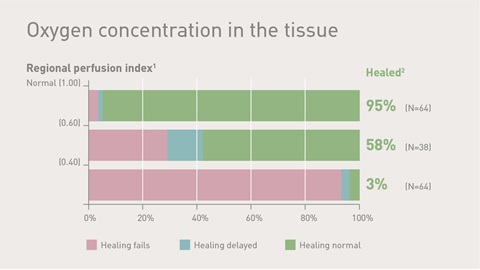
In vivo measurements has demonstrated the increase in tissue oxygenation following topical application of haemoglobin spray (Granulox) on chronic wounds:
- Haemoglobin (Hb) spray (Granulox) is sprayed. Hb diffuses into the wound exudate and starts binding oxygen
- Oxygen is readily available at the surface, and Hb binds more oxygen
- Hb diffuses within the wound bed
- Driven by the oxygen gradient, Hb releases oxygen to hypoxic regions
, contributing to multiple cycles of binding and release of oxygen - The process is reversible, and Hb can absorb more oxygen where available
Research supports the efficacy of wound oxygenation using facilitated diffusion. A EWMA group of experts has assessed the various treatment options available for addressing non-healing wounds
Clinical studies report that using Granulox haemoglobin spray leads to shorter healing time, reduced pain scores and total cost savings for healthcare providers compared to the standard of care
- Twice as many chronic wounds healed at 8–16 weeks compared to standard of care
- Time to heal diabetic foot ulcers 50% shorter than with standard of care
- More than 70% of patients reported lower average pain scores at four weeks than with standard of care in chronic wounds
- 99% less slough in chronic wounds after 4 weeks compared to 33% with standard of care
 3D imaging of a leg ulcer shows 56% O2 saturation, with large areas of deoxygenated Hb (blue) and no Hb (black)
3D imaging of a leg ulcer shows 56% O2 saturation, with large areas of deoxygenated Hb (blue) and no Hb (black)
 79% saturation, 20 minutes after Granulox (p=0.043), with large areas of oxygenated Hb (red and white)
79% saturation, 20 minutes after Granulox (p=0.043), with large areas of oxygenated Hb (red and white)
Interested in learning more about Granulox?
Mölnlycke related products
'References'